Guide to repotting bonsai

Have you ever wondered if there is a rule about when to transplant a bonsai? Can we do it whenever we want to? It seems that we can perform a transplant at any time, but in reality, transplants are done in SPRING or END OF SUMMER. Therefore, WE WILL AVOID REPOTTING IN THE MIDDLE OF SUMMER OR WINTER. If you want to learn more, don’t miss Mistral Bonsai’s guide to repotting bonsai.
As we have said before, usually we repot at the beginning of spring, when the temperature of the soil begins to rise, since it is the moment when new roots develop more easily.
There is one thing that will tell us if we have to repot in early or late spring. Deciduous bonsai are transplanted when it is still a little cold, when their leaves haven’t grown yet. In contrast, evergreen bonsai are transplanted just as spring arrives, when the temperature is getting warmer.
Bonsai repotting consists of changing the soil and rejuvenating the roots, to allow the proper development of the tree shoots. When we transplant, we prune the roots and branches of the bonsai. Normally, it is pruned a week before transplanting, to accelerate the growth of new shoots. This weakens them momentarily, so everything we do so that the bonsai recover more quickly is super important to guarantee their life.
MOST FREQUENT ERRORS DURING A TRANSPLANT
1.Transplanting too frequently. Too frequent transplantation is especially damaging to bonsai. If we repot a bonsai when the roots are not sufficiently developed, it will not have enough strength to sprout well and we will damage it.
2.Repot when the bonsai is weak. Some people think that transplanting is the solution to any problem, but it is not.
If we repot a weak tree, without looking for the cause of its weakness, it will weaken it even more. If we conclude that repotting is essential, the first thing to consider is whether it will be able to withstand the transplant.
Above all, we need to make sure of the state of the bonsai, observing it daily and if the decision to transplant is finally made, we must do it so that the tree can withstand this operation, that is, removing only the necessary part of soil and cutting only the appropriate number of roots.
3. Do not cut the roots from the bottom. Many people, when they transplant, they only cut the outer layer of the lateral roots. If they don’t also cut the roots at the bottom, the water will not reach the soil in the centre of the pot, which will weaken the tree.
4. Repotting into a pot that is too large. We have to choose a pot whose width is 80% of the total height of the bonsai.
5. Planting the bonsai too high or too deep. The trunk has to be shown in a way that makes us imagine that there are still roots hidden in the ground.
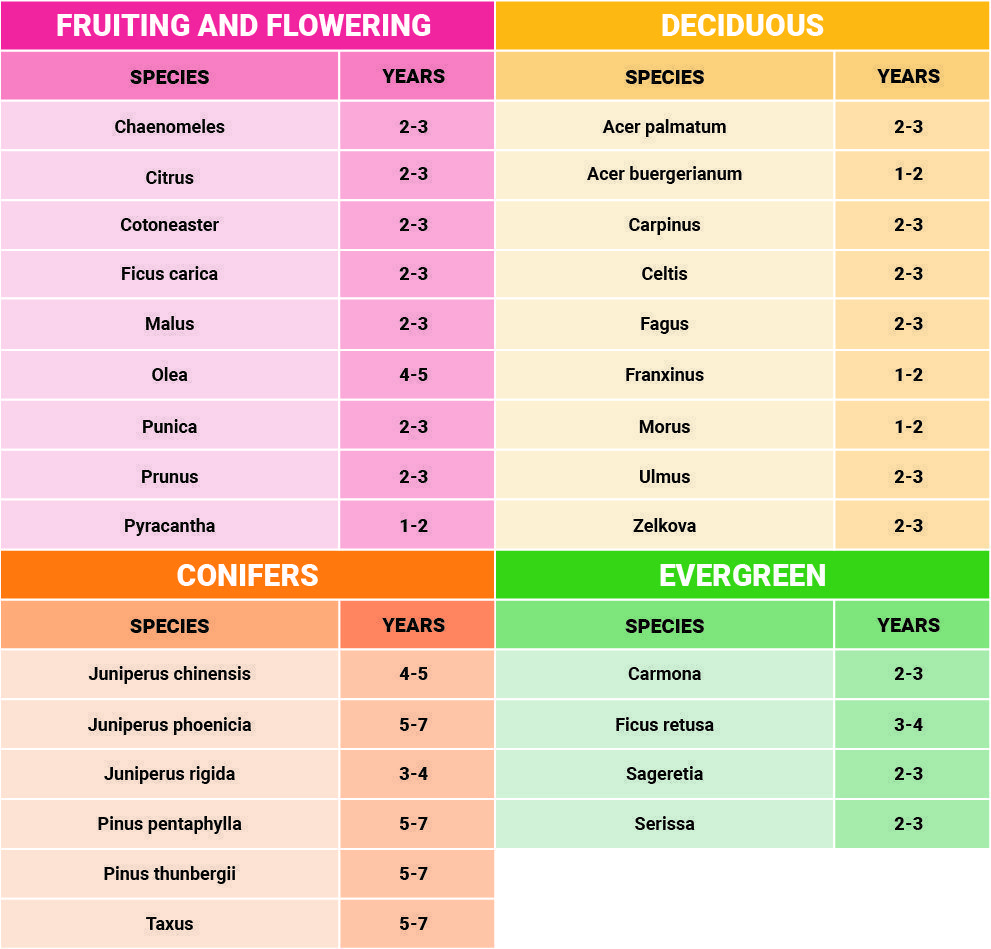
REPOTTING FREQUENCY
POST-TRANSPLANT CARE
One of the first things that influence the growth capacity of the roots after transplanting is what you do right after.
In addition, depending on where we locate it, the amount of sunlight it gets, the air temperature, the temperature of the soil in the pot, the watering frequency and technique… each of these conditions alters the capacity of the roots to grow.
To sum up, these are the most important things we should pay special attention to after repotting:
1. Protect the bonsai from the wind.
2. Water it abundantly, renewing the air in the pot.
3. Protect the bonsai from frost
Now that you have read Mistral Bonsai’s guide to repotting, we hope that you will be able to perform a perfect job so that all your bonsai will be strong, healthy and, therefore, happy.
About the Author
Mistral Bonsai
In Mistral Bonsai we are a communication team, technicians and masters committed from the first day to disseminating the wonderful art of bonsai. A world that offers many things to share. We believe that a bonsai is a tree with a soul, unique and unrepeatable. Another of our most essential pillars is, how could it be otherwise, our close commitment to the preservation of the environment and nature.
Categories
Bonsai cultivation and care (54)
Bonsai gift (2)
Bonsai pests and diseases (6)
Bonsai repotting (3)
bonsai substrates (2)
bonsai tools (1)
Bonsai work (10)
Ceramic pots (3)
Chinese culture (1)
Chinese culture (2)
Corporative Mistral Bonsai (8)
Cuidados del bonsái (22)
Cultivo del bonsái (20)
Dead wood (2)